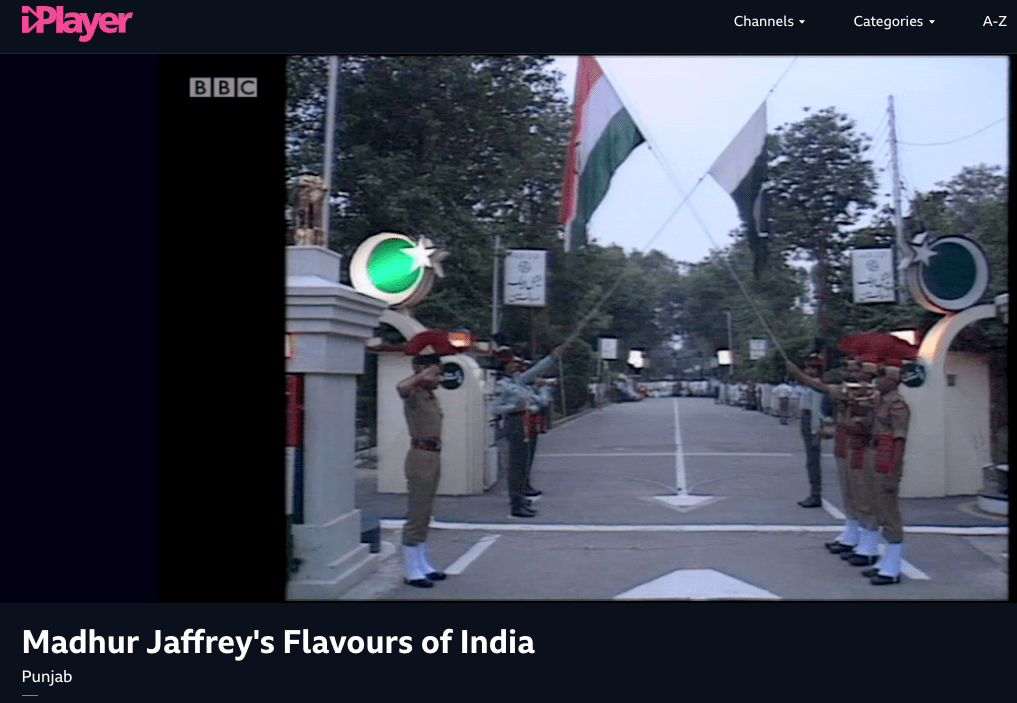
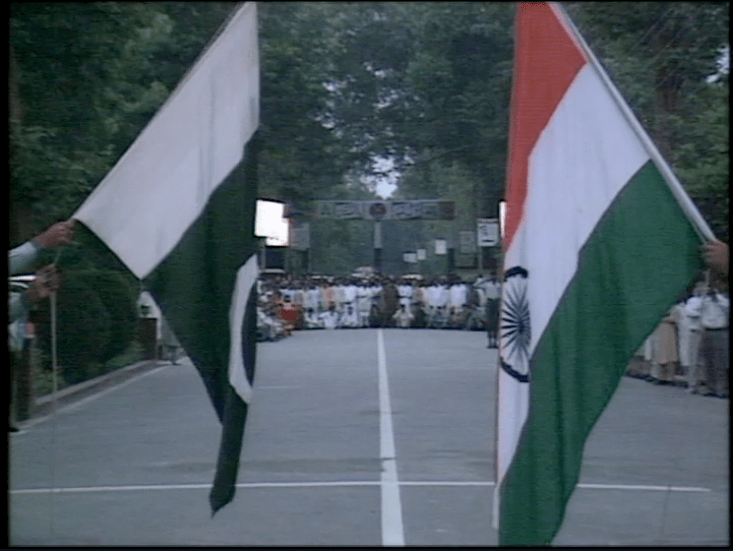Pities of Partition: Fragmented archives, claims and counter-claims, ‘actual facts’ & contested-truths, sacred and scarce, state against society, naya Pakistan & naya Bharat.
1. 31 January 1950, N. Gopalaswami Ayyangar (Minister for Transport & Railways, Govt. of Ind.) to N. Liaquat Ali Khan (Prime Minister, Govt. of Pak.):
‘I have been distressed about the action taken by the Pakistan authorities in relation to the Swaminarayan Temple at Karachi. When an allotment of a portion of the Swaminarayan Temple building was first made to a Muslim, our High-Commissioner at Karachi in December 1948, requested the Administrator, Karachi, to ensure that, for reasons of the sanctity of the temple and security of Hindus living in the temple precincts, the temple building should be reserved for the exclusive use of Hindus. By January 1949, the Administrator, Karachi, confirmed…that the Muslim allottee would be fixed up elsewhere… Later a committee of Hindus was also appointed to allot accommodation within the precincts of the temple. Lately the Administrator has abolished this committee and has withdrawn the previous assurance that the temple would be reserved for the exclusive use of Hindus. Meanwhile, further tenements in the precincts of the temple have been occupied by Muslims. The temple has not only catered for the religious and social needs of Hindus at Karachi but has also been used for accommodating Hindu refugees in transit to India…The Governments of India and Pakistan have undertaken to maintain the sanctity of the religious shrines within their territories. It is contrary to this agreement to disturb the sanctity of this temple, which is one of the important ones in Sind, particularly as Hindus in Karachi still continue to offer worship in the temple. I would strongly urge your taking suitable action in the matter…
2. 20 February 1950, N. Liaquat Ali Khan to N. Gopalaswami Ayyangar (in reply):
‘I made inquiries…The temple is surrounded by a big courtyard; all around the courtyard there are a number of tenements used as residential flats by Hindus, Muslims and others, but most of the flats do not open in the temple courtyard. A number of Muslims lived in these flats even before Pakistan was established. However, the sanctity of the temple is as well maintained as before. In order to obviate all chances of misapprehension on the part of the Hindu minority, the Administrator was willing to reserve all the flats around the temple exclusively for Hindus. Therefore, a committee of Hindus was appointed by him to recommend allotment of accommodation…It was however found that the committee took no interest in the work and allowed a number of flats to remain unoccupied. At the same time, it came to notice that the intending Hindu evacuees were transferring possession of the flats, with or without the connivance of the committee on pugree money. In view of the acute shortage of accommodation in Karachi and the recurring complaints of corruption, the Administrator had to dissolve the committee and resume the practice of making allotments direct…Preference is always given to Hindus, but when they are not available, residential accommodation cannot be allowed to remain vacant in the present-day conditions. I would reiterate that so far as the temple is concerned, its sacred position is fully maintained and the Hindus of Karachi continue to offer worship in it without let or hindrance. The High Commissioner for India recently held some of his Independence Day celebrations at the temple, which goes to show that he considered the premises exclusive enough…As regards the allocation of this whole area as a transit camp for Hindus, it is regretted that in view of the present acute shortage of accommodation, it is not possible to reserve any area in the city for this purpose. An offer is however being made to the High Commissioner for India, for allotment of sufficient land just outside Karachi for maintaining a regular transit camp…’
3. 16 March 1950, N. Gopalaswami Ayyangar to N. Liaquat Ali Khan (in reply):
‘I write to acknowledge your letter…Before replying, I had necessarily to obtain full information from our High Commissioner at Karachi in respect of the specific points you have raised…This information has since been received…You will find from [it] that the information given to you – such as that a number of Muslims lived in the flats even before Pakistan was established, that the committee of Hindus set up for advising on the allotment of accommodation took no interest in the work, that possession of some of the flats had been transferred with or without the connivance of the committee on pugree money etc. – is not in accordance with actual facts. I trust you will agree that the temple and its precincts together with the flats physically connected with it, should, for obvious reasons, be allowed to be occupied exclusively by Hindus for residential purposes and for serving as a transit camp for Hindus who pass through Karachi on their way to and back from India. You will appreciate, I am sure, the Hindu sentiment in regard to this…temple… [which] has been used as such a transit camp for over two years…I understand that our High Commissioner has been offered land at Malir for locating a transit camp. Malir is 14 miles away and the inconveniences of locating a transit camp at such a place are obvious…It is impossible for us to accept the offer and I do hope that you will be good enough to reconsider the whole matter…’
Source: File No. 12 (4)-PMS/50 (Government of Pakistan, Prime Minister’s Secretariat)
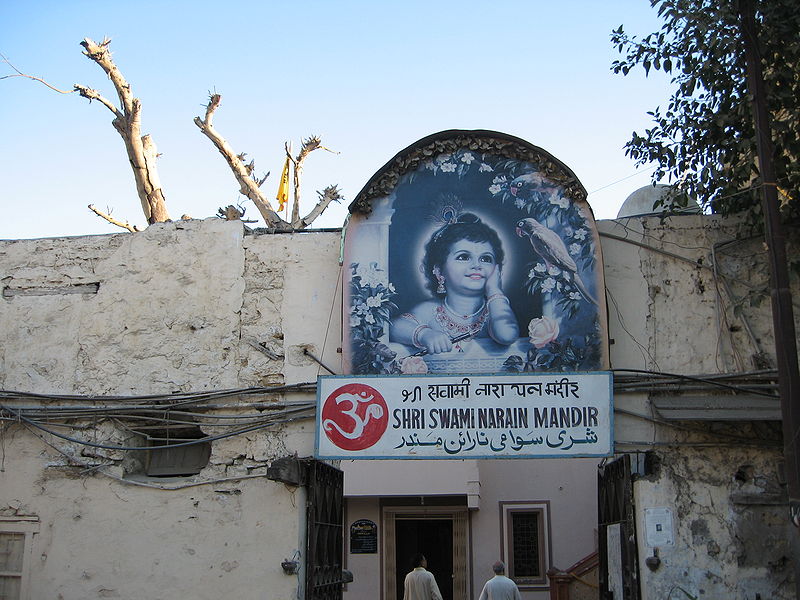
4. 12 January 2014, ‘City Faith – Shri Swaminarayan temple’, The Karachi Walla:
‘A…landmark on M.A. Jinnah Road…the temple is 200 years old according to the priest in-charge…The priest was originally from Thar. The architecture of temple is very similar to those of Jain temples in Karoonjhar range…The temple is built in the honour of Shri Swaminarayan who…lived his life in Gujrat…Naturally a link has been established between this temple and those in Gujrat and every few years, priests from both sides visit each other. The compound accommodates a Sikh Gurdwara as well. There is a sacred cowshed at the back and a gate, which leads to a neighbourhood with those fabulous balconies from yore. It is the biggest temple in Karachi and naturally a centre of celebrations during…festivals. There’s a significant Hindu population living around the temple…’
5. ‘The Shri Swaminarayan Mandir…:
‘…was built in 1849…over 32,306 square yards…on the M. A. Jinnah Road in Karachi city. The temple celebrated its anniversary of 150 years in April 2004. The temple is located at the centre of a Hindu neighbourhood in Karachi, and it is believed that not only Hindus but also adherents of Islam visit the temple…There is a sacred cowshed within the premises of this temple. [It] became a refugee camp in 1947…People who wished to settle in India from all over Sindh awaited their departure to India by ship at this temple, where they were also visited by Muhammad Ali Jinnah, during this period. In 1989, for the first time since 1947, a group of sadhus from the Shri Swaminarayan Mandir, Ahmedabad (India) visited the temple. Since then, small groups…visit every few years in a pilgrimage’.