

Sometime last year I was having dinner at the Punjab restaurant in Covent Garden, considered to the “first and oldest Punjabi, North Indian Restaurant in the UK, serving distinctive homestyle Punjabi cuisine…” It was established by Sardar Gurbachan Singh Maan in 1946, initially in Aldgate, and then shifting to Covent Garden in 1951. Maan came to the UK from Mehsumpur, in the Jalandhar District of Punjab, in what was then British India. The restaurant and café provided the familiar tastes of Punjab to the small number of Indians living in and around 1940s and 1950s London. It has since then become a go to place for many, with queues often forming outside for those hoping to chance a table for the culinary delights offered inside.
The interior is mostly simple and unfussy, but nostalgic pictures cover the wall spaces everywhere in the restaurant. They transport you to a different time and place. Quite often the pictures are of the various royal families of Punjab, whether this is the iconic Ranjit Singh or the Maharaja of Patiala; it doesn’t really matter, they provide the regal, historic and nostalgic backdrop to a bustling Punjabi meeting place in London. In between these opulent people, however, are also everyday images of South Asians and of Punjabis living in the UK.
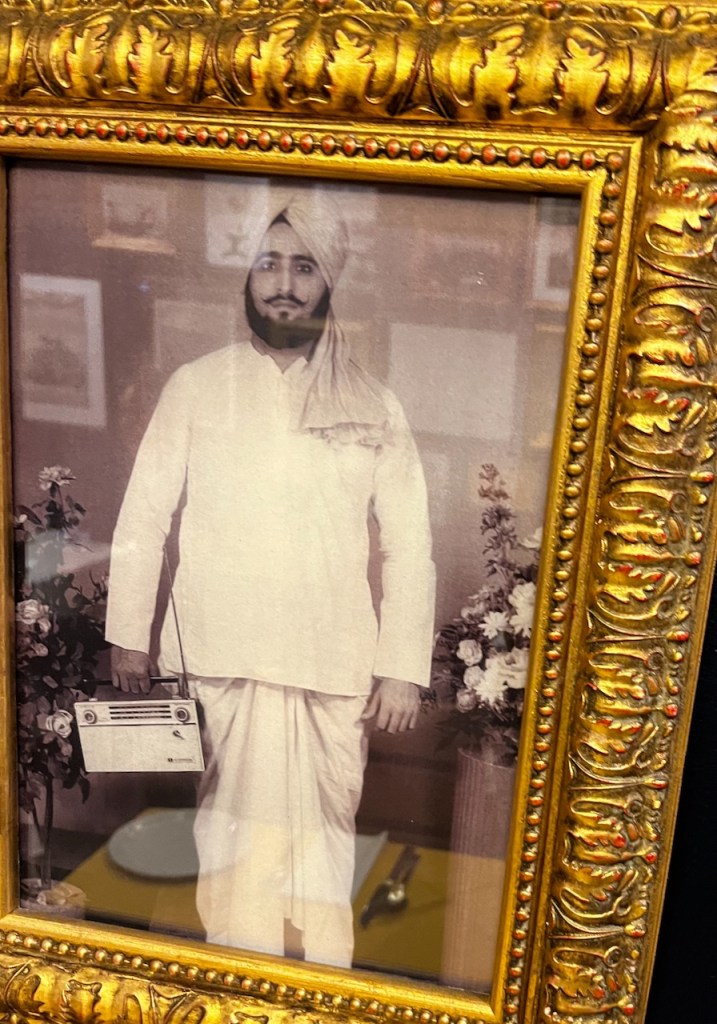
As I sat down, anxiously looking forward to my Punjabi feast, I had already decided I wanted saag, I started to curiously scan the photographs around me. Immediately a picture behind me caught my eye, it looked familiar, very familiar! It was a picture featured in a book that I did many years ago, Coming to Coventry: Stories from the South Asian Pioneers (The Herbert, 2006). The picture was of Gurdail Singh Johal, who had posed for this photograph in a traditional Punjabi kurta and tamba, while holding a transistor radio. It is a beautifully striking image, capturing the need to retain some of the cultural traits of “home”, but adapting and embracing new technologies. Like many other early migrants from Punjab, Johal migrated to Coventry in 1960 from Jalandhar, Punjab.
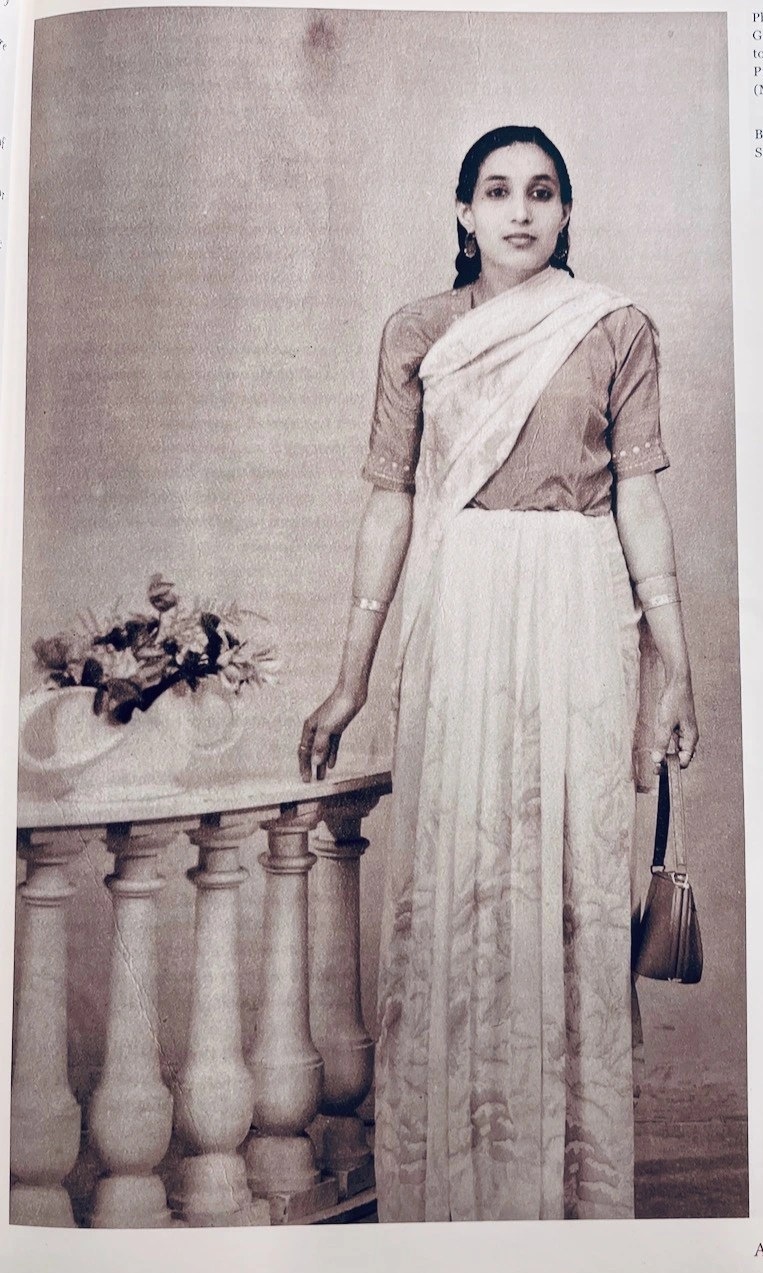
As you turn the page from Johal’s picture on page 17, there is another equally striking image of Gurmeet Kaur on page 19. This one was taken in Studio Taylor on Primrose Hill in 1959. Gurmeet is dressed in a sari, elegantly draped, and accessorised with some simple bangles and small earrings. Like Johal, Gurmeet is also holding something in her hand; the handbag conveys elegance and affluence. Mostly likely it belonged to her rather than being a prop. Both photographs have the ubiquitous floral bouquet in the backdrop, adding texture, colour and framing for the main object. Both images are important in showing how Johal and Kaur seamlessly integrate traditional dress with the modernity around them.
The studio pictures of Johal and Kaur are typical of that era where mass photography was not widespread and ownership of cameras was limited to those with means, and thus the average person could only indulge in the occasional studio photograph. Everyone dressed up and posed for the special occasion; in fact, I have many similar photographs in my own family album. It was an opportunity not only to capture a time and place, but perhaps also to preserve and show how one had progressed and advanced, especially when in a “foreign” land. It was versatile enough to share with family back home as it could be posted, and to show how they had altered their material status and to showcase the fruits of migration. Posing with a material object therefore was not just a prop in a studio picture, it was a statement about them and their class status. For the photographer it enhanced the aesthetic value of the composition, but for the people, it enhanced their status amongst their family and peers.
Discover more from BAGICHA
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.